
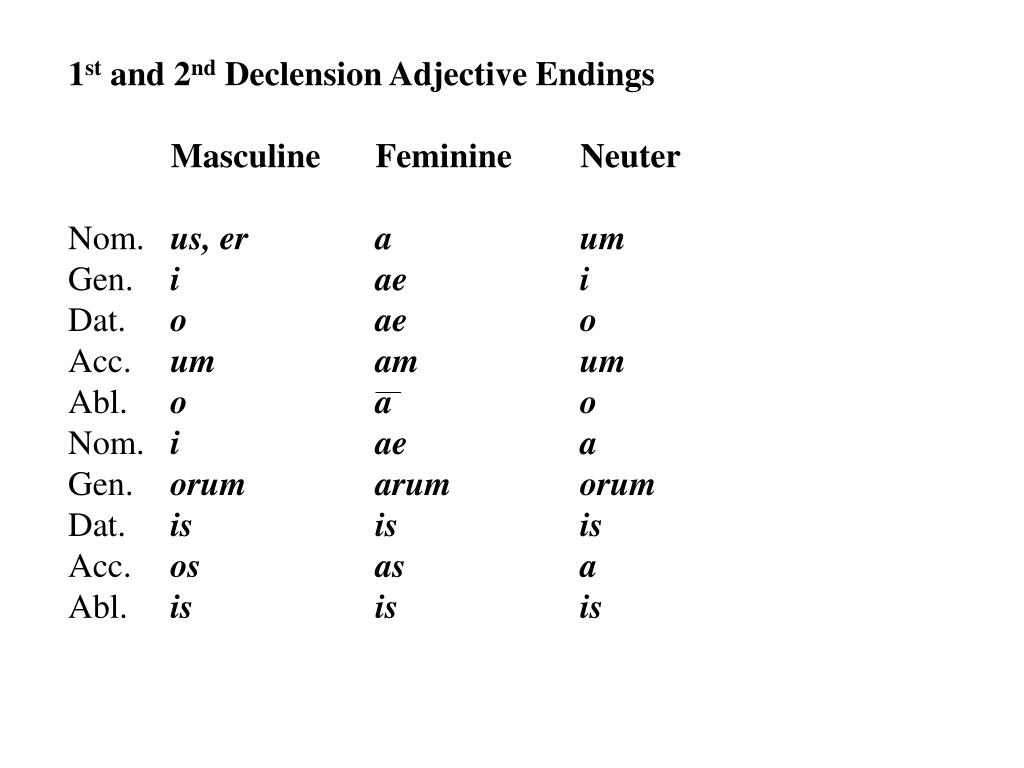
This form tells us two important pieces of information. Matris indicates the genitive singular form of the word. Mater indicates what the nominative singular form of the word is. Below we have the dictionary entry for mater: How can we determine what characteristics that a noun “in the wild” has? We need to consult what we call the dictionary entry (that is, how the noun will appear in a dictionary). Nouns can be one of six cases: nominative, genitive, dative, accusative, ablative, or vocative. Again, it will also provide information about the form that the modifying adjective must take (more on this below). Rather, the endings of the noun will change to reflect what it is doing in the sentence - whether it is a subject or direct object or the object of preposition etc. Because Latin is an inflected language, it does not rely on word order to indicate how a word functions in a sentence. For example, you wouldn’t say “the boys walks to school” rather, the plural subject “boys” must have a plural verb to agree with it: “the boys walk to school.”Ĭase indicates the function of a noun in the sentence. When nouns function as the subject of the sentence, number also helps us to determine the proper verb form to use (subject-verb agreement).

Consequently, it also plays a role in determining the form the modifying adjective may take (more on this below). Number tells us whether the noun in question is singular or plural. Nouns can be one of three of genders: masculine, feminine, or neuter. Grammatical gender is not related to biological gender (though at times they can align), but it is a classification system that allows us to determine what form the modifying adjective should take (more on this below). Latin nouns have three characteristics: grammatical gender, number, and case. Pronouns - is, ea, id | Practice Opportunity.Case Usages - Nominative and Genitive | Practice Opportunity.| Irregulars | Practice Opportunity | Substantives Nouns | Declensions | Practice Opportunity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
